Polymer latex particles, typically 50-600 nm in diameter, are used in many applications, such as paper manufacturing, water-based adhesives, printing, and coatings. Commonly, a water-based formulation that contains these polymer colloids is used, often together with other components, such as pigments for opacity and color, fillers, and rheology modifiers. Each of the polymer latex particles consists of many individual polymer chains. These water-based dispersions are applied onto a substrate as a droplet or a film, after which these systems are dried. Upon evaporation of water, the individual components will pack closely. When little water remains in between, a so-called capillary under-pressure facilitates tight packing, and if the polymer latex particles are soft, it deforms them. The last stage of the film formation process is when polymer chains from one latex particle now diffuse into a neighboring latex particle and the other way around. This process ensures that the dried film has good adhesive and mechanical properties.
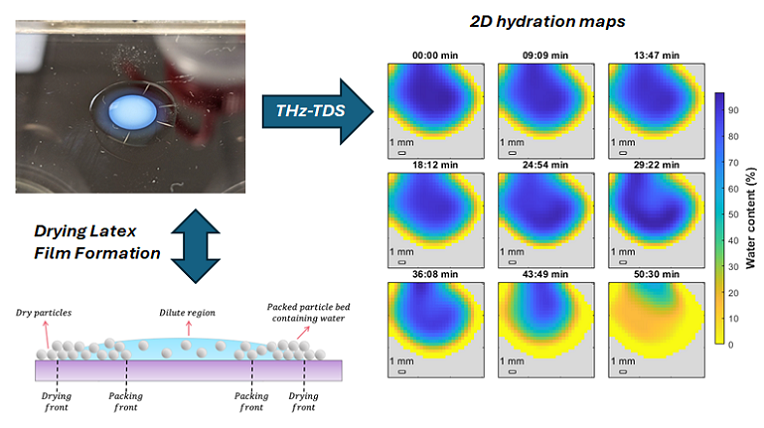
Visualizing this drying and film formation process in real time would greatly help in understanding how the properties of a dried film come about. In our paper, published in the American Chemical Society’s journal Langmuir, we used TeraHertz Time-Domain Spectroscopy (THz-TDS) to map the water content spatially in real-time during the drying process.